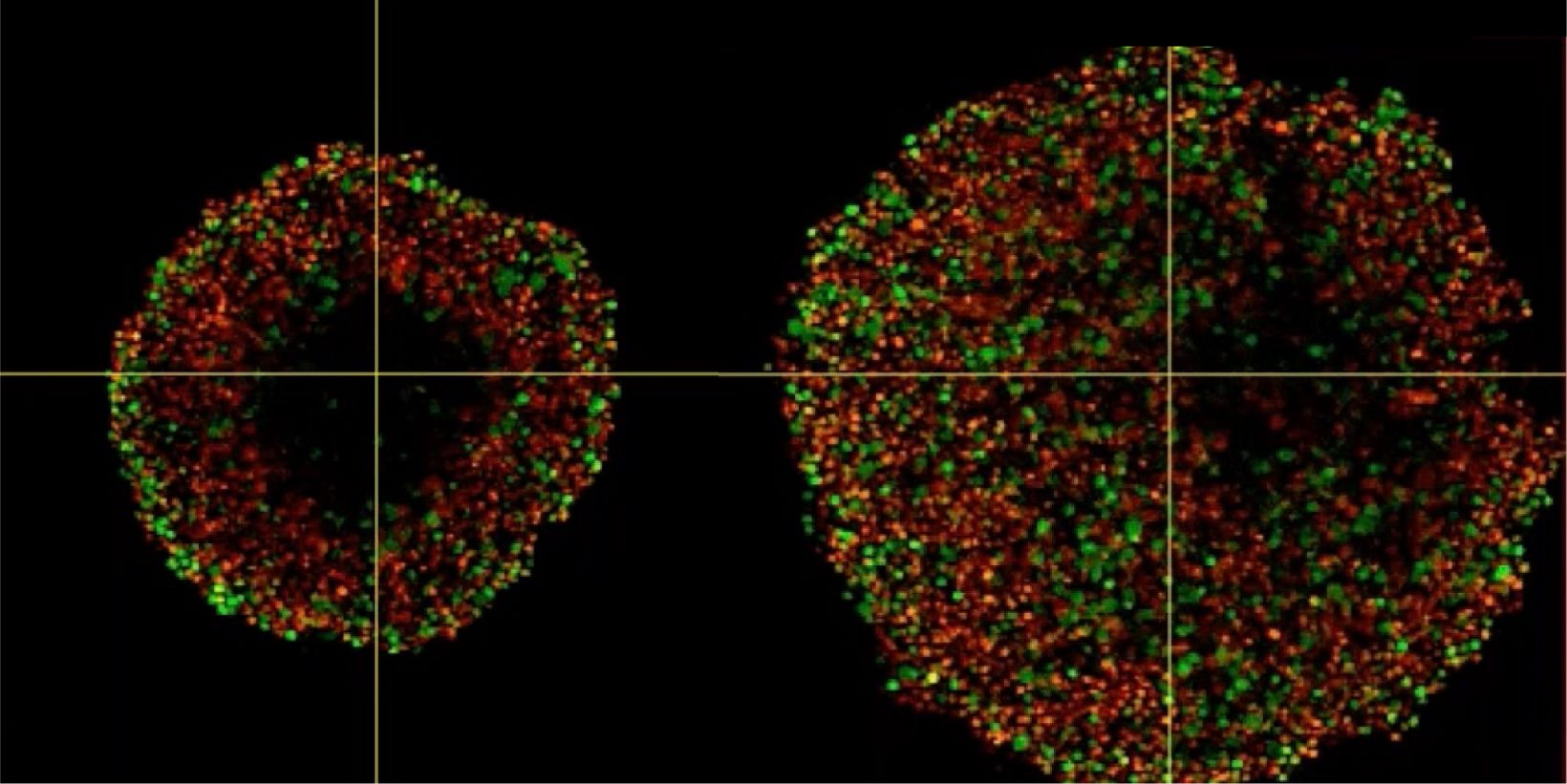
Phenotypic tumour heterogeneity arising due to differentially cycling cell populations has been implicated in increased therapy resistance. This phenomenon cannot be assessed in adherent cell culture, where microenvironmental conditions are homogeneous. Thus, we utilise melanoma spheroids to model the 3D tumour microenvironment including the extracellular matrix (ECM) and study spheroid structure, necrotic region, individual cell arrangement within and gene expression patterns. We achieve this by exploiting the fluorescence ubiquitination cell cycle indicator (FUCCI) system to monitor cell cycle stages as a surrogate marker for phenotypic tumour heterogeneity, tissue clearing and confocal microscopy using FV3000.
Investigating Spheroid Architecture Using the FV3000 Confocal MicroscopePhenotypic tumour heterogeneity arising due to differentially cycling cell populations has been implicated in increased therapy resistance. This phenomenon cannot be assessed in adherent cell culture, where microenvironmental conditions are homogeneous. Thus, we utilise melanoma spheroids to model the 3D tumour microenvironment including the extracellular matrix (ECM) and study spheroid structure, necrotic region, individual cell arrangement within and gene expression patterns. We achieve this by exploiting the fluorescence ubiquitination cell cycle indicator (FUCCI) system to monitor cell cycle stages as a surrogate marker for phenotypic tumour heterogeneity, tissue clearing and confocal microscopy using FV3000. | |
相关产品激光扫描共聚焦显微镜 FV3000
| |
Investigating Spheroid Architecture Using the FV3000 Confocal Microscope
Related Videos
相关产品
FV3000
- 所提供的两种配置为仅装有常规振镜扫描单元的FV3000显微镜和装有常规/共振混合
- 型扫描单元的FV3000RS
- 可对所有通道进行全新、高效、精确的TruSpectral全真光谱检测
- 经过优化,可以完成具有高灵敏度和低光毒性的活细胞成像操作