The performance of any optical imaging instrument is perhaps best judged by the quality of the images produced. This gallery contains digital videos captured with the FV300 and FV1000 under a variety of experimental conditions and scanning modes. In several cases, the raw optical section data has been processed by deconvolution, three-dimension volume rendering, and other related techniques.
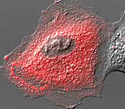
Rabbit Kidney Cells with mCherry Actinin
Alpha-actinin may be one of the proteins involved in attachment of the actin cytoskeletal network to the plasma membrane in a wide spectrum of cell types.
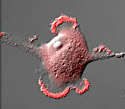
Rabbit Kidney Cells with mCherry Actin
Actin is a highly conserved globular protein that differs in amino acid sequence by less than 20 percent in species ranging from algae to humans.
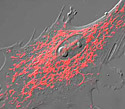
Gray Fox Lung Fibroblast Cells with mKO Mitochondria
The mitochondrion has its own circular DNA and reproduces independently of the cell in which it is found.
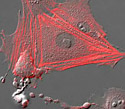
Gray Fox Lung Fibroblast Cells with mKO Actin
Actin filaments, composed of polymerized globular actin subunits, are found throughout the cytoplasm of the cell.
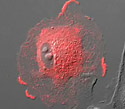
Rabbit Kidney Epithelial Cells with mKO Actin
The rate of growth of an actin filament is influenced by the rate of hydrolysis of the ATP-containing actin monomers.

Rabbit Kidney Epithelial Cells with mKO Vinculin
Focal adhesions are large assemblies of macromolecules through which the cell can anchor itself to the extracellular matrix.
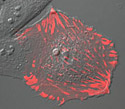
Gray Fox Lung Fibroblast Cells with mTagRFP Zyxin
Focal adhesions are complex structures composed of many protein components that serve as an anchor for the cell.
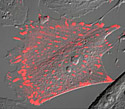
Gray Fox Lung Fibroblast Cells with mKusabira Orange Zyxin
Zyxin is found in fibroblasts, smooth muscle and pigmented retinal epithelium.

Rabbit Kidney Epithelial Cells with mKO Histone H2B
The cell nucleus is well defined and surrounded by the nuclear envelope (or membrane) during interphase.
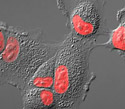
Rabbit Kidney Epithelial Cells with mCherry Histone H2B
In prophase, major changes also occur in the cytoplasm, including disassembly of the cytoplasmic microtubules.
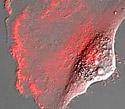
Human Glioblastoma Epithelial Cells with mCherry Actin
Actin is a globular protein found in all eukaryotic cells, with the exception of nematode sperm.
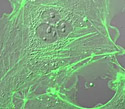
Opossum Kidney Epithelial Cells with EYFP Actin
Cell movement by pseudopodia depends upon actin filament construction and disassembly.

Gray Fox Lung Fibroblast Cells with Kindling Red Mitochondria
Mitochondrion has its own circular DNA (similar to the DNA of prokaryotes).
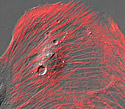
Rat Thoracic Aorta Cells with JRed Actin
Three primary functions are performed by actin within the structure of the cell.
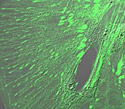
Rat Thoracic Aorta Cells with EGFP Actinin
Alpha actinins belong to the spectrin gene superfamily which represents a diverse group of cytoskeletal proteins.
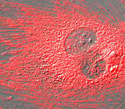
Rat Thoracic Aorta Cells with mCherry Actin
Actin has the capability of quickly assembling into long polymer rods called microfilaments.
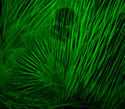
Rat Thoracic Aorta Cells with Dronpa Actin
Actin filaments in animal cells are organized into two different styles: bundles and weblike (gel-like) networks.
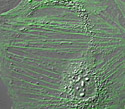
Rat Thoracic Aorta Cells with Dronpa Actin
Actins from different species even as far apart as plants, yeasts, and mammals bear a striking similarity in amino acid sequence.
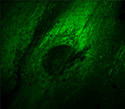
Rat Thoracic Aorta Cells with Dronpa ER
The extensive endoplasmic reticulum network (ER) serves as a factory for the production of almost all of the cell’s lipids.
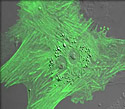
African Mongoose Cells with EYFP Actin
The amino acid sequence that comprises actin (a highly conserved protein) in humans is very similar to that found in yeasts and plants.
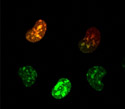
Baby Hamster Kidney Cells with Kaede Nucleus Fluorescence
The nucleus is found in most eukaryotic cells and houses most of the cell's genetic material.
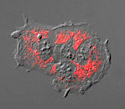
Baby Hamster Kidney Cells with DsRed Mitochondria
Anywhere from one to several thousand mitochondria may be present in a cell, depending on the metabolic requirements.

Baby Hamster Kidney Cells with Kaede Nucleus
Nearly all the DNA in a eukaryotic cell is sequestered in the nucleus, which is about 10% of the total cell volume.
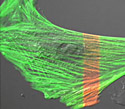
Gray Fox Lung Fibroblast Cells with dEos Actin
Actin serves three distinct functions: cytoskeleton, motility, and several transport processes.
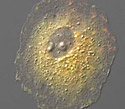
Rabbit Kidney Epithelial Cells with tandem-dimer Eos Vinculin
Large assemblies of macromolecules are known as focal adhesions.
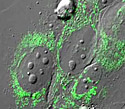
Human Osteosarcoma Epithelial Cells with EYFP Mitochondria
A cell contains up to several thousand mitochondria, depending on the metabolic requirements of the organism.
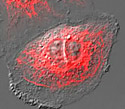
Rabbit Kidney Epithelial Cells with mKusabira Orange Keratin
Cytokeratins are a class of intermediate filaments found in the cytoplasmic cytoskeleton of epithelial tissues.
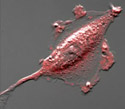
Rabbit Kidney Epithelial Cells with mCherry FAK
Focal adhesions are found on the cell membrane where the cytoskeleton interacts with proteins of the extracellular matrix.
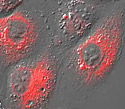
Rabbit Kidney Epithelial Cells with tdTomato ER
The endoplasmic reticulum, an organelle that is part of all eukaryotic cells, is comprised of an interconnected network of tubules, vesicles and cisternae.
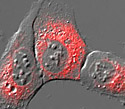
Human Osteosarcoma Epithelial Cells with DsRed ER
The endoplasmic reticulum is one of three components of the GERL system, with the Golgi apparatus and the lysosomes.
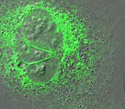
Human Osteosarcoma Epithelial Cells with EYFP ER
Endoplasmic reticulum is suspended in the cytosol, one of the three major elements which makes up the cytoplasm.
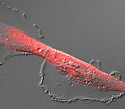
Human Glioblastoma Epithelial Cells with mCherry Actinin
Small amounts of alpha-actinin or filamin have a significant effect on the physical properties of a solution of actin filaments.