The Olympus Microscopy Resource Center galleries include images of fluorescent specimens, as well as darkfield, phase contrast, and Hoffman modulation contrast photomicrographs. In addition, the gallery features streaming video and images from featured microscopists.
Grey Fox Lung Fibroblast Cells (FoLu Line)
The FoLu line of cells was established from the lung tissue of an adult female grey fox (Urocyon cinereoargenteus). The cells exhibit many of the typical characteristics associated with fibroblasts and are primarily used in virus studies. Many lung-derived cell lines similar to FoLu have also been utilized in studies focusing upon the short- and long-term effects of cigarette smoke, and this particular line is potentially useful for such research as well.
Mongolian Gerbil Lung Fibroblast Cells (GeLu Line)
Lung tissue of a rodent native to parts of Africa and Asia, the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus), served as the source of the initial cells from which the GeLu fibroblast line was established. The tissue sample was excised from a 403-day-old female.
Raccoon Uterus Fibroblast Cells (Pl 1 UT Line)
Studies have shown that Pl 1 UT cells are susceptible to an array of viruses, including herpes simplex virus, reovirus 3, and vesicular stomatitis (Ogden strain). The line is, therefore, commonly utilized in the propagation of such viruses for research purposes and has been particularly useful in investigations of feline and canine viral diseases.
Swiss Mouse Embryo Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus Transfected Fibroblast Cells (CRE BAG 2 Line)
CRE BAG 2 is a fibroblast cell line that was developed from the NIH 3T3 embryonic Swiss mouse cell line, which was transfected with Moloney murine leukemia virus-derived proviral genomes carrying complementary mutations in the gag-pol or env regions. The genomes were altered at the 3’ end of the provirus and contained a deletion of the psi sequence needed for the efficient encapsidation of retroviral genomes into virions.
Embryonic Albino Swiss Mouse Fibroblast Cells (3T3 Line)
Established by George Todaro and Howard Green in 1962 from disaggregated Swiss mouse (Mus musculus) embryo tissue, the 3T3 cell line is a standard fibroblast cell line used in a wide spectrum of research and industrial biomedical applications. Variants of the initial cell line have been tested and found negative for ectromelia virus (mousepox), but most are susceptible to polyoma and simian virus 40 (SV40). In addition, 3T3 cells are negative for the viral enzyme reverse transcriptase, indicating the lack of integral retrovirus genomes.
Horse Dermal Fibroblast Cells (NBL-6 Line)
Initiated from the dermal tissue of a 4-year-old female horse (Equus caballus) of the quarterhorse strain, the NBL-6 cell line (also called the E. Derm line) has played an important role in equine viral arteritis (EVA) research. EVA is a contagious respiratory disease caused by a small, enveloped RNA virus. The fibroblast cell line is also commonly utilized to propagate viruses for equine vaccine production.
Human Fetal Lung Fibroblast Cells (MRC-5 Line)
MRC-5 cells are a line of human lung fibroblast cells established in the 1960s by J. P. Jacobs. Studies have demonstrated that the cells are susceptible to several different viruses, including vesicular stomatitis (Indiana strain), poliovirus 1, and herpes simplex. The MRC-5 line is frequently used in laboratories for many different applications, such as in vitro cytotoxicity testing, the development of vaccines, and as a transfection host for investigation of viruses and viral diseases.
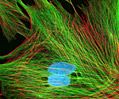
Indian Muntjac Deer Skin Fibroblast Cells
A fibroblast cell line established from a skin biopsy of an adult male, the Indian Muntjac deer epidermis line is commonly used in laboratories around the world, especially for chromosome studies. The normal (non-transformed) Indian Muntjac cell line is susceptible to the herpes simplex virus, vaccinia virus, and vesicular stomatitis virus (Indiana strain).
 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer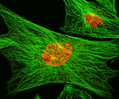 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer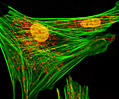 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer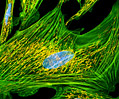 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer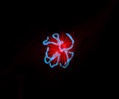 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer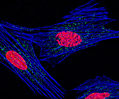 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer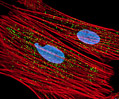 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer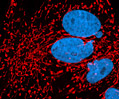 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer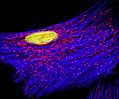 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer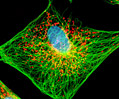 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer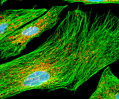 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer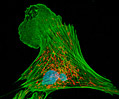 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer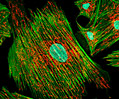 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer
Normal African Green Monkey Kidney Fibroblast Cells (CV-1 Line)
Investigators working with simian virus 40 (SV40) or in the field of AIDS research often utilize CV-1 cells, which were initially used in studies of the Rous sarcoma virus (RSV). A team led by F. C. Jensen established the CV-1 cell line in the early 1960s. The cells from which the line was initiated were sampled from the renal tissue of an African green monkey (Cercopithecus aethiops). CV-1 cells are popularly employed in transfection experiments and are known to be susceptible to a wide array of viruses.
Transformed African Green Monkey Kidney Fibroblast Cells (COS-7 Line)
Adherent growth to both glass and plastic surfaces is characteristic of COS-7 cells in culture. The line, which is often utilized as a transfection host, retains the CV-1 trait of complete permissiveness for the lytic growth of SV40 and supports the replication of the tsA209 strain of the virus at 40 degrees Celsius as well as SV40 mutants with deletions in the early region. COS-7 cells are a popular research tool, especially for transfection experiments with recombinant plasmids.