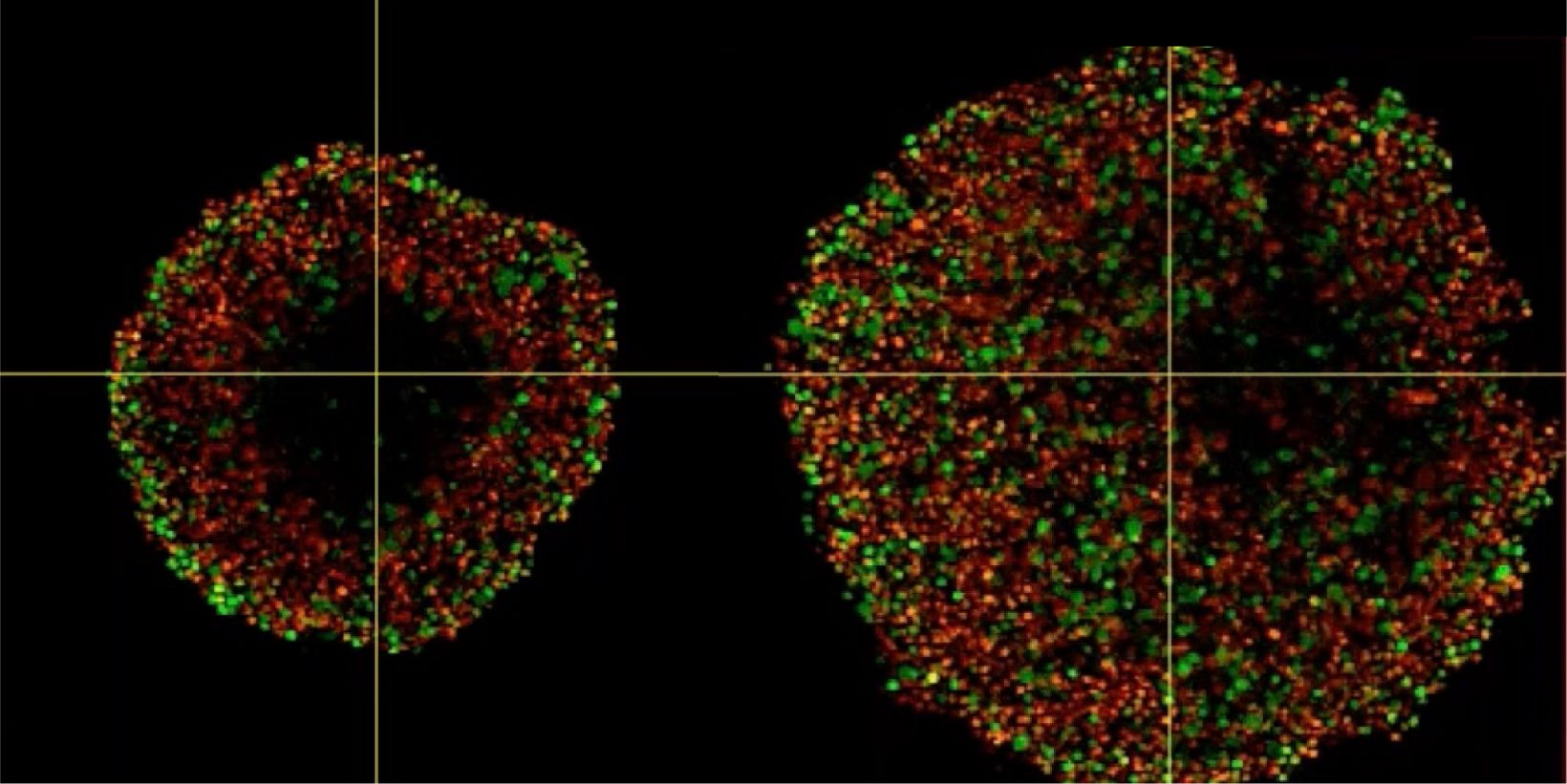
Phenotypic tumour heterogeneity arising due to differentially cycling cell populations has been implicated in increased therapy resistance. This phenomenon cannot be assessed in adherent cell culture, where microenvironmental conditions are homogeneous. Thus, we utilise melanoma spheroids to model the 3D tumour microenvironment including the extracellular matrix (ECM) and study spheroid structure, necrotic region, individual cell arrangement within and gene expression patterns. We achieve this by exploiting the fluorescence ubiquitination cell cycle indicator (FUCCI) system to monitor cell cycle stages as a surrogate marker for phenotypic tumour heterogeneity, tissue clearing and confocal microscopy using FV3000.
Investigating Spheroid Architecture Using the FV3000 Confocal MicroscopePhenotypic tumour heterogeneity arising due to differentially cycling cell populations has been implicated in increased therapy resistance. This phenomenon cannot be assessed in adherent cell culture, where microenvironmental conditions are homogeneous. Thus, we utilise melanoma spheroids to model the 3D tumour microenvironment including the extracellular matrix (ECM) and study spheroid structure, necrotic region, individual cell arrangement within and gene expression patterns. We achieve this by exploiting the fluorescence ubiquitination cell cycle indicator (FUCCI) system to monitor cell cycle stages as a surrogate marker for phenotypic tumour heterogeneity, tissue clearing and confocal microscopy using FV3000. | |
関連製品共焦点レーザー走査型顕微鏡 FV3000
| |
Investigating Spheroid Architecture Using the FV3000 Confocal Microscope
Related Videos
関連製品
FV3000
- ガルバノスキャナーのFV3000と、ガルバノ/レゾナントのハイブリッドキャナーのFV3000RS
- 高感度・高精度のTruSpectral分光検出器
- 新開発マルチチャンネルモードによる16チャンネルのアンミキシング