The Olympus Microscopy Resource Center galleries include images of fluorescent specimens, as well as darkfield, phase contrast, and Hoffman modulation contrast photomicrographs. In addition, the gallery features streaming video and images from featured microscopists.
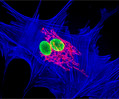
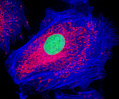
African Water Mongoose Skin Fibroblast Cells (APM Line)
The APM cell line was established at The Naval Biosciences Laboratory (NBL) in Oakland, California from the skin of an African water mongoose (Atilax paludinosus). An elusive animal, the African water mongoose exhibits solitary, nocturnal habits and is a good swimmer, although it frequently lingers in shallow waters where it catches shellfish, crabs, frogs, and similar aquatic and semi-aquatic animals for food. APM mongoose cells exhibit fibroblast morphology and, similar to other fibroblast lines, are among the easiest cells to grow in culture. Cell biologists hypothesize that the ability of fibroblasts to grow so readily outside of the body is associated with their central role in the healing of wounds, which necessitates their proliferation when confronted with injury or other less than optimal conditions. Fibroblasts are also generally considered to exhibit relatively solitary lifestyles, which some have suggested may also be a factor in their favorable growth in culture.
 APM Line
APM Line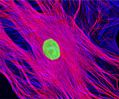 APM Line
APM Line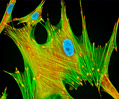 APM Line
APM Line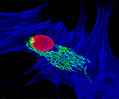 APM Line
APM Line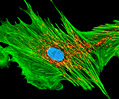 APM Line
APM Line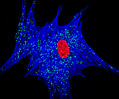 APM Line
APM Line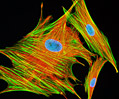 APM Line
APM Line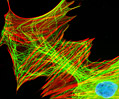 APM Line
APM Line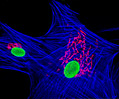 APM Line
APM Line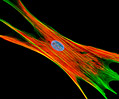 APM Line
APM Line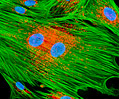 APM Line
APM Line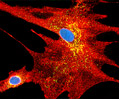 APM Line
APM Line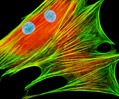 APM Line
APM Line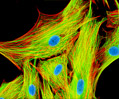 APM Line
APM Line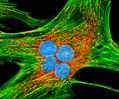 APM Line
APM Line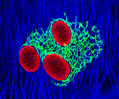 APM Line
APM Line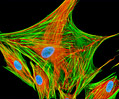 APM Line
APM Line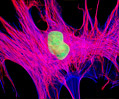 APM Line
APM Line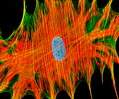 APM Line
APM Line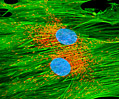 APM Line
APM Line
Baby Hamster Kidney Fibroblast Cells (BHK-21 Line)
The BHK-21 fibroblast cell line was established in March of 1961 by I. A. Macpherson and M. G. P. Stoker. The widely used line is a subclone (clone 13) of a parental line derived from the kidneys of five unsexed, 1-day-old hamsters. These hamsters were of the species Mesocricetus auratus and are commonly known as Syrian golden hamsters. Subsequent to 84 days of continuous cultivation, interrupted only for an 8-day preservation by freezing, clone 13 was initiated by single-cell isolation. BHK-21 cells are susceptible to human adenovirus D, reovirus 3, and vesicular stomatitis virus (Indiana strain), but are resistant to poliovirus 2. In addition, the cells are negative for reverse transcriptase, indicating the lack of integral retrovirus genomes. The BHK-21 line has been utilized as a host for transformation with expression vectors containing selectable and amplifiable marker DNAs and is also useful for transfections.
Embryonic Rat Thoracic Aorta Medial Layer Myoblast Cells (A-10 Line)
The clonal cell line A-10 was derived by B. Kimes and B. Brandt from the thoracic aorta of an embryonic rat (Rattus norvegicus) from the established strain DB1X. The thoracic aorta is a branch of the descending aorta, which transports blood from the heart to the other organs and parts of the body. This arbitrary anatomic entity is generally considered to extend from the arch of the aorta to the diaphragm.
 A-10 Line
A-10 Line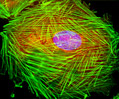 A-10 Line
A-10 Line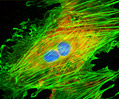 A-10 Line
A-10 Line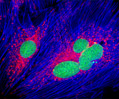 A-10 Line
A-10 Line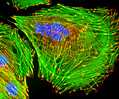 A-10 Line
A-10 Line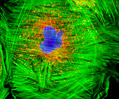 A-10 Line
A-10 Line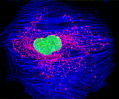 A-10 Line
A-10 Line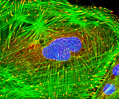 A-10 Line
A-10 Line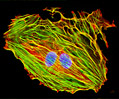 A-10 Line
A-10 Line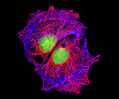 A-10 Line
A-10 Line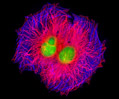 A-10 Line
A-10 Line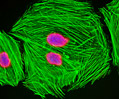 A-10 Line
A-10 Line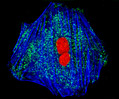 A-10 Line
A-10 Line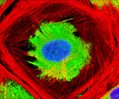 A-10 Line
A-10 Line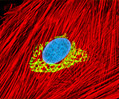 A-10 Line
A-10 Line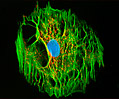 A-10 Line
A-10 Line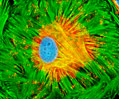 A-10 Line
A-10 Line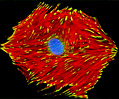 A-10 Line
A-10 Line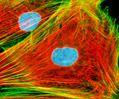 A-10 Line
A-10 Line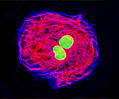 A-10 Line
A-10 Line
Embryonic Swiss Mouse Fibroblast Cells (3T3 Line)
Established by George Todaro and Howard Green in 1962 from disaggregated Swiss mouse (Mus musculus) embryo tissue, the 3T3 cell line is a standard fibroblast cell line used in a wide spectrum of research and industrial biomedical applications. Variants of the initial cell line have been tested and found negative for ectromelia virus (mousepox), but most are susceptible to polyoma and simian virus 40 (SV40). In addition, 3T3 cells are negative for the viral enzyme reverse transcriptase, indicating the lack of integral retrovirus genomes. Within the cytoplasm, lysophosphatidylcholine (lyso-PC) induces AP-1 activity and c-jun N-terminal kinase activity (JNK1) by a protein kinase C-independent pathway. Contact inhibited, a confluent monolayer of 3T3 cells yields approximately 40,000 cells per square centimeter.
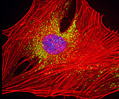 3T3 Line
3T3 Line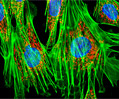 3T3 Line
3T3 Line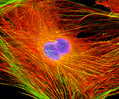 3T3 Line
3T3 Line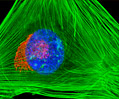 3T3 Line
3T3 Line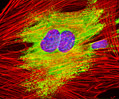 3T3 Line
3T3 Line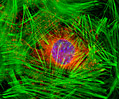 3T3 Line
3T3 Line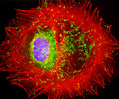 3T3 Line
3T3 Line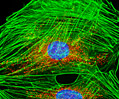 3T3 Line
3T3 Line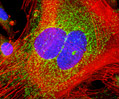 3T3 Line
3T3 Line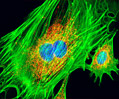 3T3 Line
3T3 Line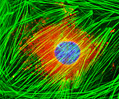 3T3 Line
3T3 Line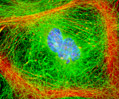 3T3 Line
3T3 Line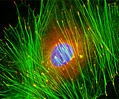 3T3 Line
3T3 Line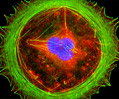 3T3 Line
3T3 Line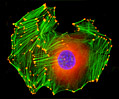 3T3 Line
3T3 Line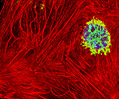 3T3 Line
3T3 Line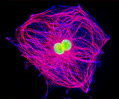 3T3 Line
3T3 Line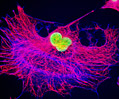 3T3 Line
3T3 Line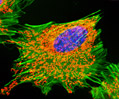 3T3 Line
3T3 Line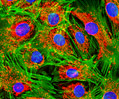 3T3 Line
3T3 Line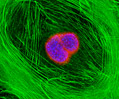 3T3 Line
3T3 Line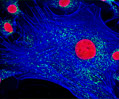 3T3 Line
3T3 Line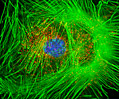 3T3 Line
3T3 Line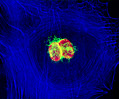 3T3 Line
3T3 Line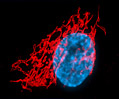 3T3 Line
3T3 Line
Horse Dermal Fibroblast Cells (NBL-6 Line)
The NBL-6 cell line, also known as E. Derm, was derived from the dermis of a 4-year-old female horse (Equus caballus) of the quarterhorse strain. The cells, which appear to senesce after approximately 40 passages, are susceptible to herpes simplex, reovirus 3, vesicular stomatitis (Ogden strain), and vaccinia, but resist adenovirus 5, coxsackievirus A9 and B5, and poliovirus 2. NBL-6 cells, which are negative for reverse transcriptase and exhibit typical fibroblast morphology, have been utilized for a variety of studies, as well as for virus propagation for equine vaccines. The cell line has been particularly important in research focusing upon equine viral arteritis (EVA), a contagious viral disease that affects horse populations worldwide and appears to be increasing in incidence.
Human Cortical Neuronal Cells (HCN-1A Line)
The source for the HCN-1A cell line was cortical tissue removed from a patient undergoing hemispherectomy for intractable seizures. The patient was an 18-month-old female suffering from unilateral megalencephaly. Also known as hemimegalencephaly, this condition is characterized by the overgrowth of all or part of one of the cerebral hemispheres. HCN-1A cells stain positively for a number of neuronal markers including neuron specific enolase. They are also positive for tubulin, vimentin, somatostatin, glutamate, gamma aminobutyric acid, cholecystokinin-8, and vasoactive intestinal peptide. The cells are negative, however, for glial fibrillary acidic protein and myelin basis protein. HCN-1A cells can be induced to differentiate when cultured with a mixture of nerve growth factor, dibutyryl cyclic adenosine monophosphate, and 1-isobutyl-3-methylxanthine. Differentiation is accompanied by mature morphology and a deceleration of growth.
Human Fetal Lung Fibroblast Cells (MRC-5 Line)
The MRC-5 cell line is commonly utilized in vaccine development, as a transfection host in virology research, and for in vitro cytotoxicity testing. Initiated in September 1966 by J. P. Jacobs, the cell line was derived from the human lung tissue of a 14-week-old male fetus aborted from a 27-year-old woman. MRC-5 cells, which grow adherently in culture and exhibit fibroblast morphology, may double in population size 42 to 46 times before the onset of senescence. They are susceptible to poliovirus 1, herpes simplex, and vesicular stomatitis (Indiana strain). The line is, however, negative for reverse transcriptase, indicating the lack of integral retrovirus genomes.
Indian Muntjac Deer Skin Fibroblast Cells
A fibroblast cell line established from a skin biopsy of an adult male, the Indian Muntjac deer epidermis line is commonly used in laboratories around the world, especially for chromosome studies. Members of the family Cervidae, Muntjacs are barking deer that emit their characteristic sound when they feel threatened or alarmed. The normal (non-transformed) Indian Muntjac cell line is susceptible to the herpes simplex virus, vaccinia virus, and vesicular stomatitis virus (Indiana strain), but is resistant to poliovirus 1. Recent tests have demonstrated that the cells produce both detectable bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) antigens and infectious BVDV virions. Muntjac cells are negative for reverse transcriptase, indicating the lack of integral retrovirus genomes.
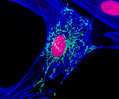 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer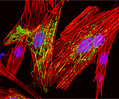 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer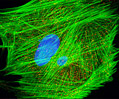 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer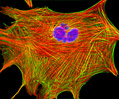 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer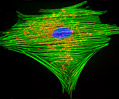 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer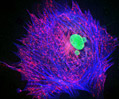 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer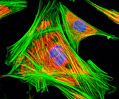 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer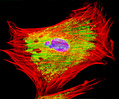 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer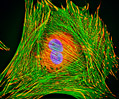 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer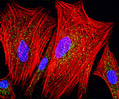 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer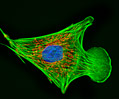 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer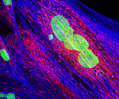 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer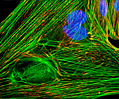 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer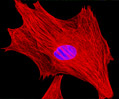 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer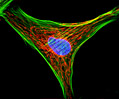 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer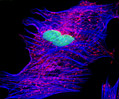 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer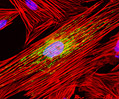 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer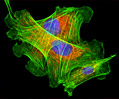 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer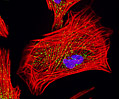 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer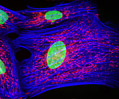 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer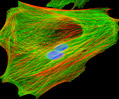 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer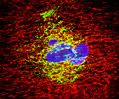 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer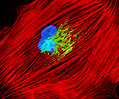 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer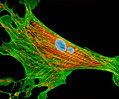 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer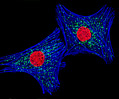 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer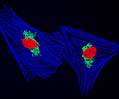 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer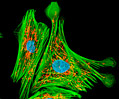 Indian Muntjac Deer
Indian Muntjac Deer
Transformed Chicken Embryo Fibroblast Cells (UMNSAH/DF-1 Line)
UMNSAH/DF-1 is a spontaneously immortalized chicken (Gallus gallus) cell line derived from 10-day-old East Lansing strain (ELL-0) eggs. To develop the line, primary chicken embryonic fibroblasts were dissociated and grown in culture. The fibroblasts were passaged until they began to senesce. The UMNSAH/DF-1 chicken embryo fibroblast line is useful as a substrate for virus propagation, recombinant protein expression, and recombinant virus production. The line is susceptible to a number of viruses, including Meleagrid herpes virus 1, fowlpox virus, reovirus, avian sarcoma leukemia virus, and Rous sarcoma virus. The cells are not, however, tumorigenic in immunosuppressed mice, but do form colonies in a semisolid medium. UMNSAH/DF-1 cells are negative for reverse transcriptase, indicating the lack of integral retrovirus genomes.