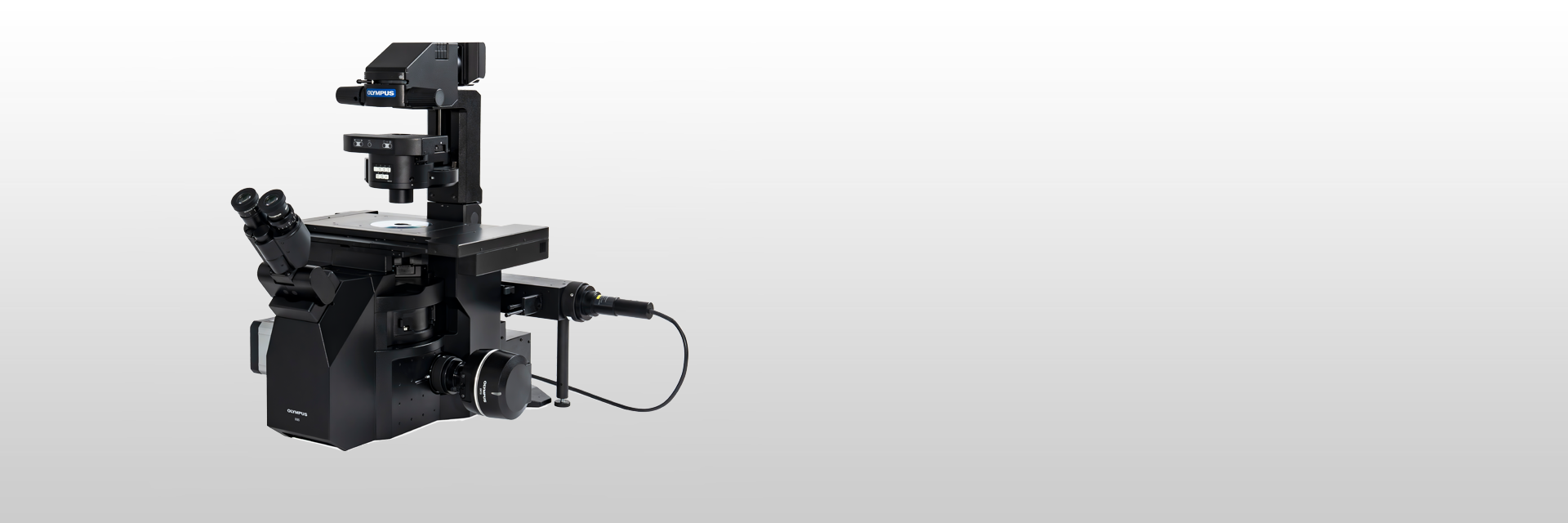
| Clear, Fast, Accurate Live Cell ImagingThe IXplore™ IX85 Live inverted microscope system delivers precise live cell imaging, helps reduce photobleaching, and enhances cell viability for physiological experiments. And with an industry-leading 26.5mm field number (FN), the IXplore™ IX85 Live helps you acquire clear, accurate images faster than ever before. |
|---|
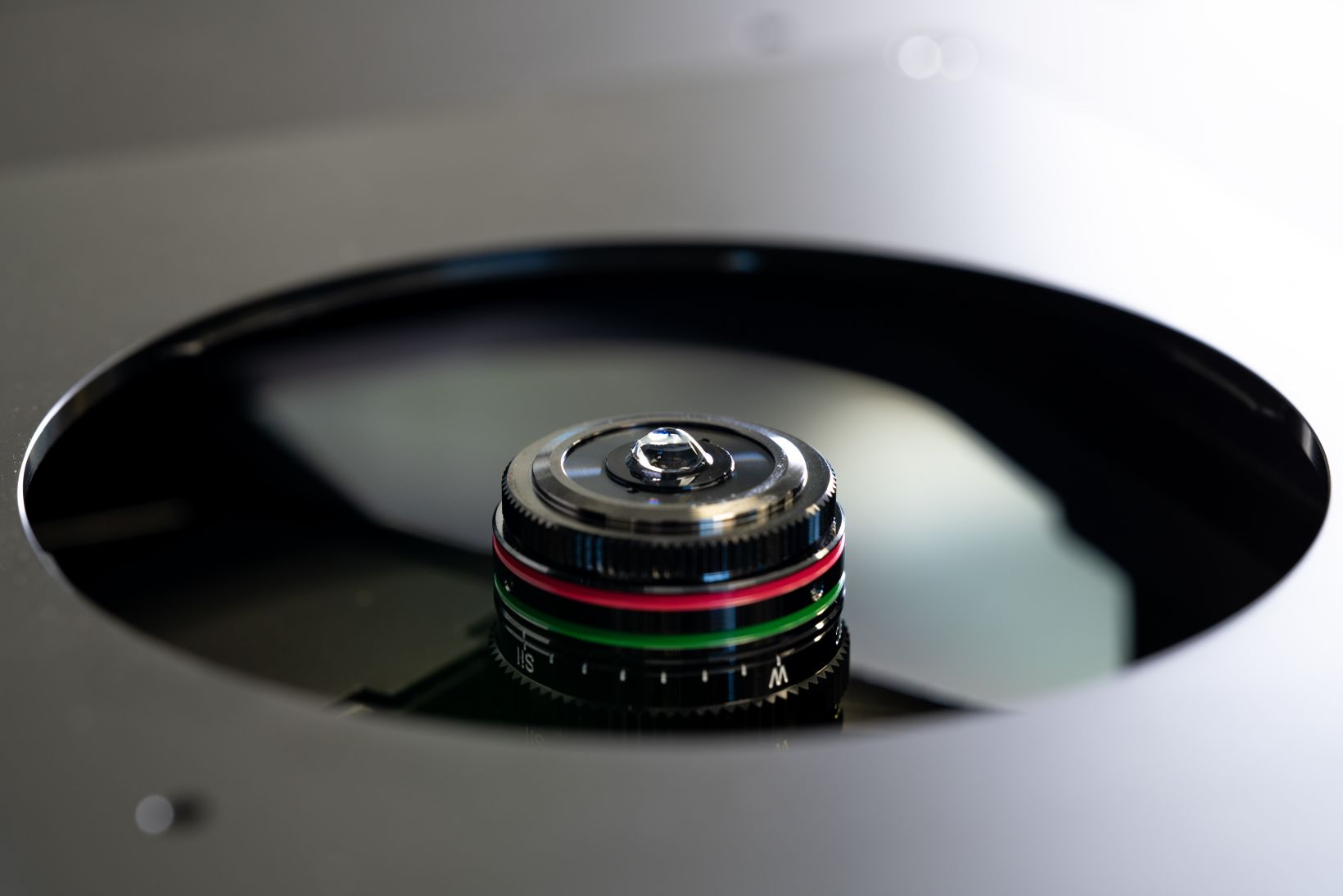
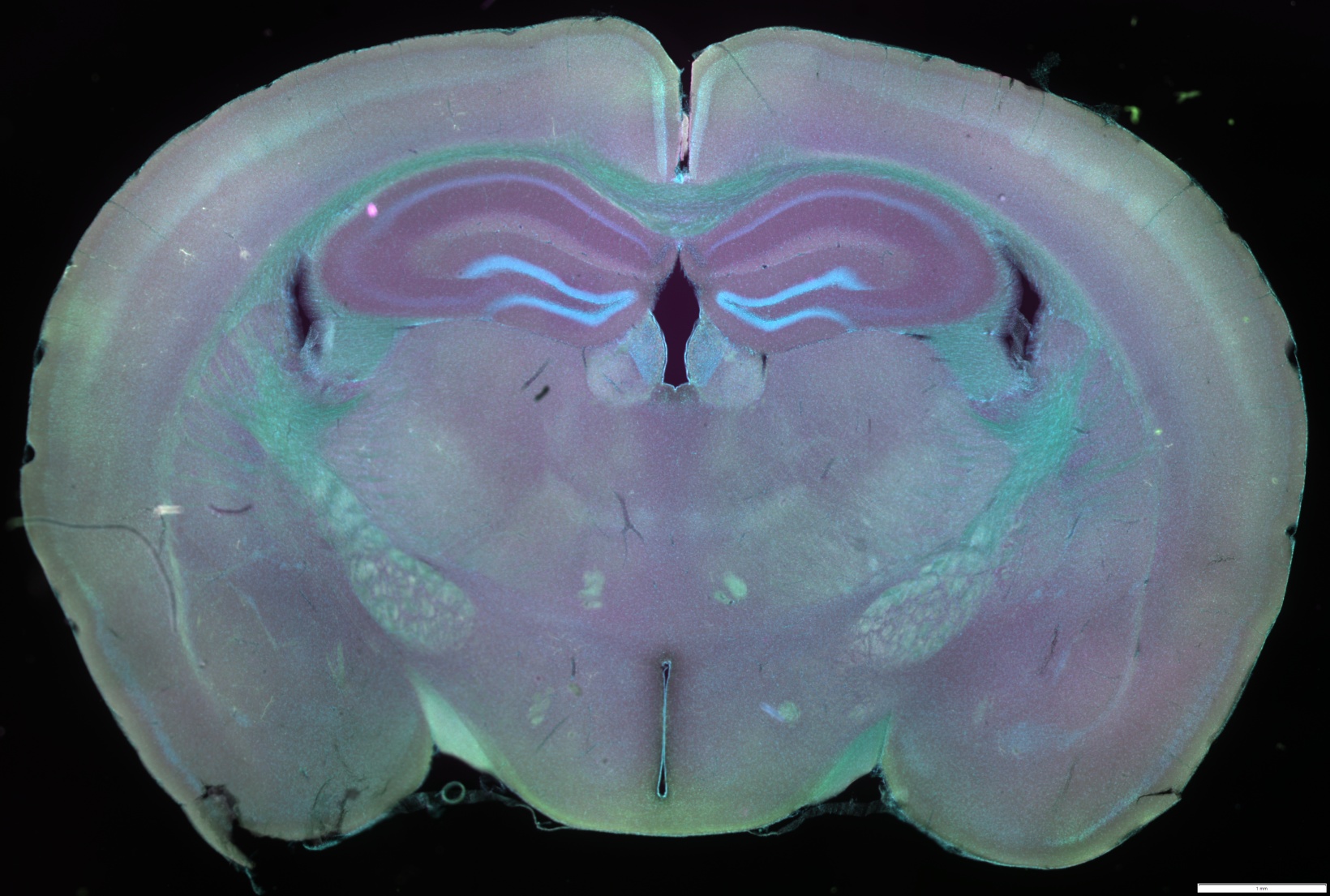
A New Standard in Image Depth and Objective UsabilityEvident’s silicone oil immersion objectives allow you to capture clearer images of living specimens during sophisticated timelapse experiments. These objectives help reduce the spherical aberration caused by refractive index mismatch and enable high-resolution observation deep inside living tissue. Our new multi-immersion objective (LUPLAPO25XS) introduces groundbreaking new immersion technology. This objective combines all of the advantages of our silicone oil immersion objective with new levels useability. With silicone gel pad technology, you can get the quality of silicone immersion oil with the useability of a dry objective.
| |
|---|---|
The new LUPLAPO25XS enhances workflows for organoids, 3D cell culture, well-plates, and a wide range of applications, with crystal-clear imaging and no compromise in usability. See deeper into your samples and reveal structures that were previously out of reach with a high NA and long working distance. | |
XYZ image comparison between Left: LUPLAPO25XS (Silicone gel) and Right: UPLXAPO20X (Dry)
|
Stable, Trustworthy Imaging OutputsLive cell imaging requires significant time and resources—it’s important that your lab has the right microscope system. The IXplore™ IX85 Live system offers enhanced rigidity and reduces the effects of vibration and temperature on your microscope. This also facilitates reliable timelapse imaging by helping maintain the desired focus position on the Z-axis. Pair the IXplore™ IX85 Live system with our TruFocus™ Z-drift compensator to capture cellular dynamics through high-precision, multipoint timelapse images that are never out of focus or misaligned. |
|---|
Carefully Maintaining Live SamplesLive cells require careful maintenance—we offer a variety of microscope-based incubation systems designed to meet your changing research needs. Box-type incubation systems* enable timelapse observations over several days by enclosing a portion of your microscope within the incubator. Shorter experiments can be completed with stage-top microscope CO2 incubation systems* that are fitted to your stage and can be easily removed when not in use by your team. Both incubation systems can be precisely controlled (temperature, humidity, and CO2 concentration) to maintain a constant environment surrounding your dish or well-plates. This maintains cell activity and significantly improves the reliability of your timelapse observations—ultimately providing you with better data. *Third-party products. | See how Jutta Bulkescher, Microscopy Specialist at the Center for Protein Research/Danish Stem Cell Center, University of Copenhagen, conducts a wide range of research at her facility and how incubation systems enables her to reliably perform stem cell analysis while maintaining cells under strict conditions. |
Cultured Cos 7 cell
| Close Monitoring of Cell Migration GrowthUse our cellSens Object Tracking and Count and Measure solutions to analyze the movement and division of live cells in timelapse or Z-stack image sets. Confluency Checker tools are a proven way for you to measure confluency on phase contrast images as well as fluorescence. |
|---|
Improve Experiment Efficiency with Advanced DeconvolutionWith our cellSens Dimension software, you can utilize live 2D deblurring for preview and acquisition to enable exceptional focusing on your thickest specimens. More advanced TruSight deconvolution is also available that uses an iterative algorithm to produce improved resolution, contrast, and dynamic range. To further improve experiment efficiency, you can define deconvolution processing as a macro function in the Graphical Experimental Manager (GEM). |
|---|
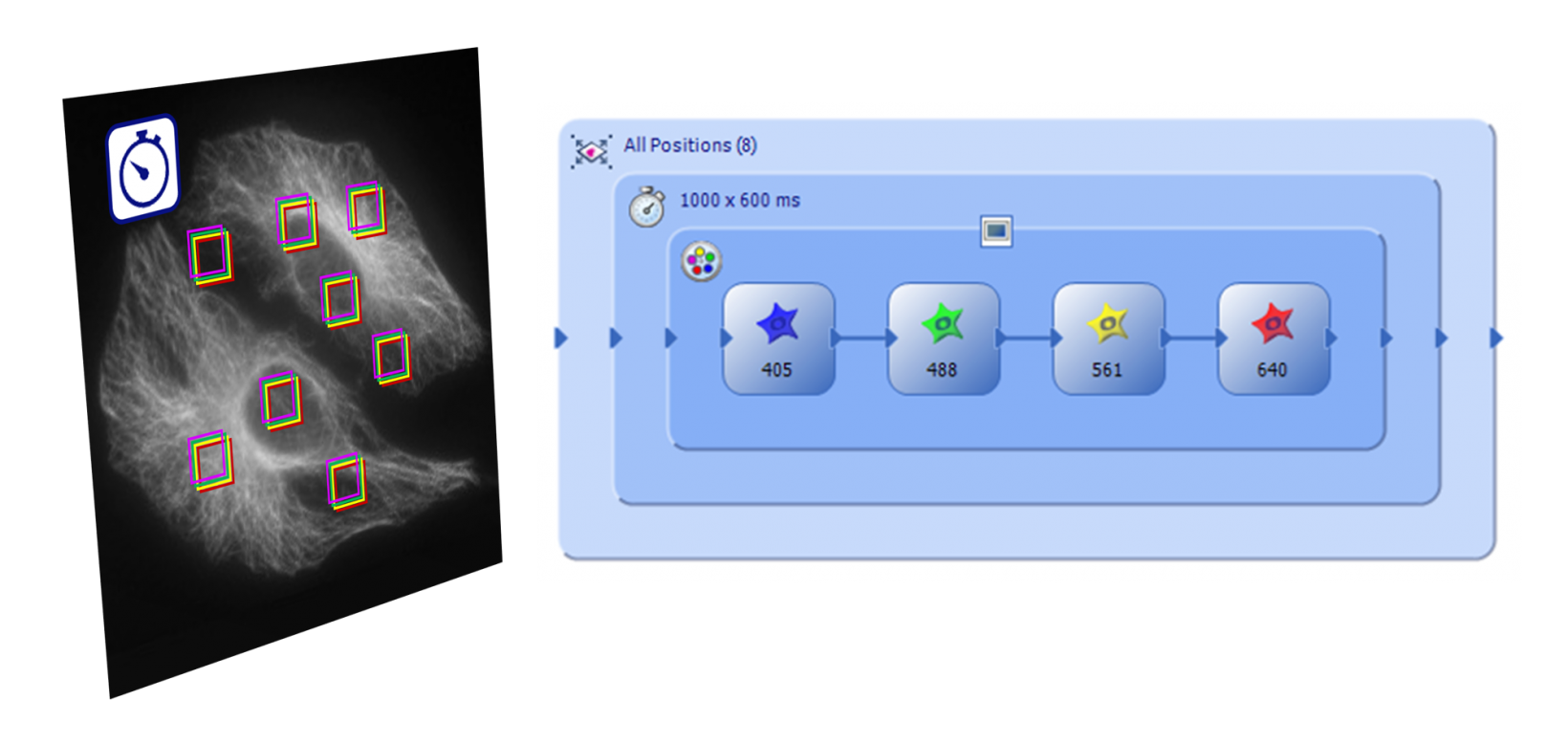
Fully Automated EfficiencyThe Graphical Experimental Manager (GEM) of cellSens Dimension software allows fully automated multidimensional observation (X, Y, Z, T, wavelength, and positions) and helps make experiment setup easier than ever. To further increase efficiency, you can also define macro functions, including deconvolution processing, in the GEM. |
|---|
IXplore™ IX85 Automated Inverted Microscope PlatformThe foundation of our IXplore IX85 Live system, the IXplore™ IX85 delivers the largest FN in the industry and an array of advanced end-to-end imaging features, allowing you to see and capture more than ever before while dramatically reducing acquisition times. Experience exceptional speed, clarity, and reliability with the IXplore IX85 microscope system. |
See how Evident Microscopes Have been used in live cell researchS. Wakayama, et al. Chemical labelling for visualizing native AMPA receptors in live neurons. Nature Communications (April 7, 2017). S. N. Cullati, et al. A bifurcated signaling cascade of NIMA-related kinases controls distinct kinesins in anaphase. The Journal of Cell Biology (June 19, 2017). L. Gheghiani, et al. PLK1 activation in late G2 sets up commitment to mitosis. Cell Reports (June 6, 2017). D. Nakane and T. Nishizaka, et al. Asymmetric distribution of type IV pili triggered by directional light in unicellular cyanobacteria. PNAS (June 5, 2017). T. A. Redchuk, et al. Near-infrared optogenetic pair for protein regulation and spectral multiplexing. Nature Chemical Biology (March 27, 2017). S. Barzilai, et al. Leukocytes breach endothelial barriers by insertion of nuclear lobes and disassembly of endothelial actin filaments. Cell Reports (January 17, 2017). J. Humphries, et al. Species-independent attraction to biofilms through electrical signaling. Cell (January 12, 2017). A. Prindle, et al. Ion channels enable electrical communication in bacterial communities. Nature (October 21, 2015). K. G. Harris, et al. RIP3 regulates autophagy and promotes coxsackievirus B3 infection of intestinal epithelial cells. Cell Host & Microbe (August 13, 2015). |
*1 Although it became one of the most important cell lines in medical research, it’s imperative that we recognize Henrietta Lacks’ contribution to science happened without her consent. This injustice, while leading to key discoveries in immunology, infectious disease, and cancer, also raised important conversations about privacy, ethics, and consent in medicine.
|
IXplore Microscopes |
Need assistance? |
Sorry, this page is not
available in your country.