High-Resolution Imaging of Bone Cell Interactions Using the FLUOVIEW FV3000 Confocal Microscope and an X Line 40X Oil Immersion Objective
Bone constantly remodels using a balance of osteoclastic bone resorption and osteoblastic bone formation. However, certain health factors can cause an imbalance, leading to brittle bone in bone diseases such as osteoporosis. To understand the mechanism of bone remodeling, it is important to observe the interactions between osteoclasts and osteoblasts.
In this study, we prepared a mouse tibial cross-section (Figure 1) and closely observed osteoclasts and osteoblasts in the boundary zone between bone marrow and cortical bone. This application typically requires using a low-magnification objective to capture a wide field of view in order to identify a region of interest, followed by using a high-magnification oil immersion objective to observe the details in higher resolution. However, this approach can be difficult since you may lose the region of interest while switching objectives.
Here, we found the region of interest in a wide field of view and observed the fine structures in high-resolution using only a 40X oil immersion objective without switching objectives.
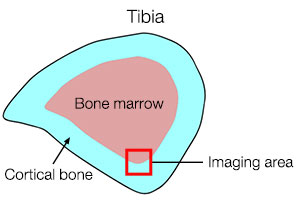
Figure 1: Tibial cross-section
High-Resolution Imaging of Bone Cell Interactions Using an X Line 40X Oil Immersion Objective (UPLXAPO40XO)
We observed the boundary zone between the bone marrow and cortical bone in a mouse tibial cross-section, as well as the contact site (* in Figure 2a) of osteoblasts (green) with vascular endothelial cells (yellow), and the interaction site (# in Figure 2a) of osteoblasts with osteoclasts (red). The wide field of view of the 40X oil objective enabled us to acquire an image that shows where the high-magnification image is located on the overview image (Inset of Figure 2a).
Using scan zoom, we could closely observe the interaction site of osteoblasts with osteoclasts (Figure 2b). The image quality obtained using the X Line UPLXAPO40XO objective was almost the same as the one obtained using a UPLSAPO60XO conventional objective (Figure 2c).
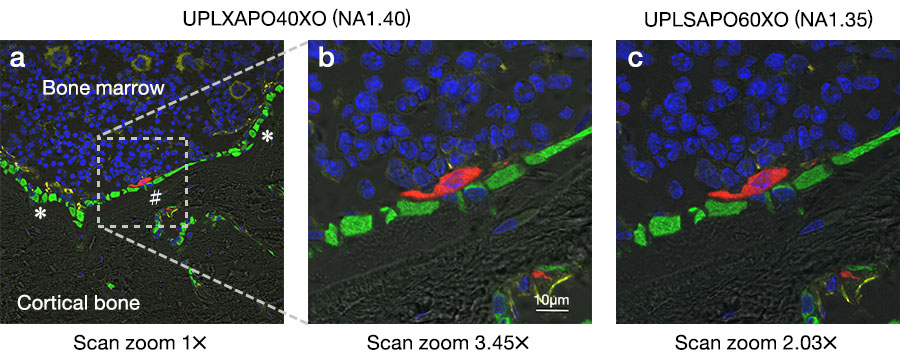
Figure 2: Fluorescent images of a mouse tibial cross-section
Image obtained using 1x scan zoom with a UPLXAPO40XO objective
Image obtained using 3.45x scan zoom with a UPLXAPO40XO objective
Image obtained using 2.03x scan zoom with a UPLSAPO60XO objective
Imaging conditions
Microscope: FV3000 system
Objective: UPLXAPO40XO (UPLSAPO60XO used for reference)
Lasers: 488 nm (Alexa Fluor 488, green), 561 nm (Alexa Fluor 568, red), 640 nm (Alexa Fluor 647, yellow)
How the FV3000 Confocal Microscope Facilitated Our Experiment
High-Performance Imaging with X Line Objectives
X Line objectives’ high numerical aperture (NA) enables them to gather more light for brighter, higher resolution images. |  |
Acquire High Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) Images Under Low Excitation Light
| Using proprietary spectral detection technology, the FV3000 confocal microscope's TruSpectral detectors combine high sensitivity with spectral flexibility to detect even dim fluorophores. TruSpectral detectors incorporate up to four channels of GaAsP photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) with up to 45% quantum efficiency, enabling users to view samples that were too dim to view with conventional equipment. Peltier cooling reduces background noise by 20% for high SNR images under very low excitation light. | 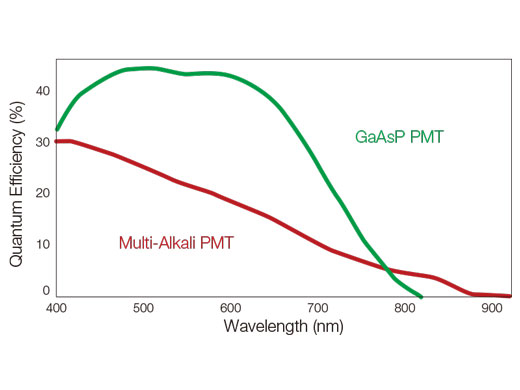 |
Comment by Dr. Yukiko Kuroda
| It was difficult to find the interaction sites during high-resolution imaging of osteoclast and osteoblast interactions when switching between a low-magnification dry objective for wide field of view and a UPLSAPO60XO objective for high-resolution imaging. Another challenge was adding oil during the imaging process. When we used the UPLSAPO60XO objective for the entire imaging process, it took a long time to find the region of interest due to the narrow field of view. This study demonstrates that we could successfully find the interaction sites and acquire high-resolution images equivalent to ones captured with the UPLSAPO60XO objective using only a 40X oil immersion objective (UPLXAPO40XO) with a high numerical aperture (NA) equivalent to UPLSAPO60XO. As a result, we could efficiently observe the interactions between osteoclasts and osteoblasts using only the UPLXAPO40XO objective. |
Acknowledgments
This application note was prepared with the help of Dr. Yukiko Kuroda. She is an instructor at Keio University and was responsible for the images in this study.
Products Related to This Application
was successfully added to your bookmarks
Maximum Compare Limit of 5 Items
Please adjust your selection to be no more than 5 items to compare at once
Not Available in Your Country
Sorry, this page is not
available in your country.
