Use of Low Chromatic Aberration Objective PLAPON60XOSC for Quadruple Immunofluorescence of Brain Tissue
Use of Low Chromatic Aberration Objective PLAPON60XOSC for Quadruple Immunofluorescence of Brain Tissue
Introduction
Labelling molecules with a fluorescent dye before acquiring fluorescence images with an optical microscope such as confocal microscope is established as the most common experimental method for visualizing the localization of molecules in biological tissues and cells.
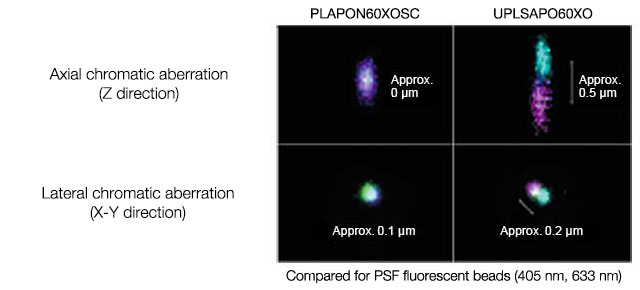
However, accurate visualization of multiple intercellular co-localizations was difficult in a single specimen because color shifts caused by chromatic aberration of the microscopic objective lenses made it difficult to use fluorescent dyes for accurate visualization of the intercellular co-localization in UV and near infrared regions. Olympus’ low chromatic aberration objective PLAPON60XOSC lens provides accurate visualization of fluorescence-labelled molecules with few color shifts, even in UV and near infrared regions. The following introduces cases where four types of fluorescent antibody were used to visualize the co-localization of fluorescence-labelled molecules accurately in a single specimen.
Performance Comparison of PLAPON60XOSC and UPLSAPO60XO
An application of the Low Chromatic Aberration Objective - Quadruple Immunofluorescence of Brain Tissue
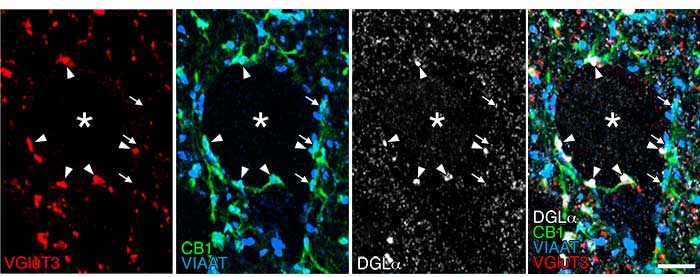 | |
| Quadruple immunofluorescence of brain tissue: Picture (1) |
VIAAT staining (Alexa Fluor405, blue)
CB1 staining (Alexa Fluor488, green) VGluT3 staining (Cy3, red) DGLα staining (Alexa Fluor647, white) |
Cannabinoid synthetase DGLα (white) and cannabinoid receptors CB1 (green) are clustered around the pyramidal cell somata (asterisk) in mouse basal amygdala, forming invaginating synapses (arrowhead) with a unique invagination structure. These invaginating synapses express vesicular inhibitory amino acid transporter (VIAAT) (blue) and vesicular glutamate transporter-3 (VGluT3) (red), which suggests that they have the neurochemical properties of both inhibitory and excitatory transmitters—GABA and glutamine acid, respectively. In contrast, the CB1-positive, VIAAT-positive common type of inhibitory synapses did not express VGluT3 if DGLα clusters were not formed around them, showing that they have the neurochemical properties of GABA only. Scale bar: 5 μm.
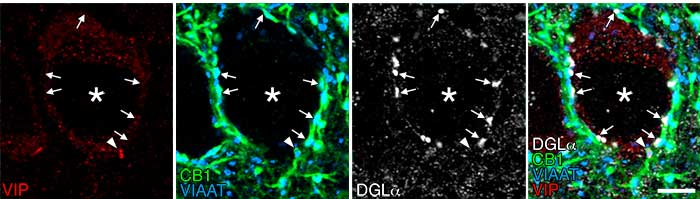 | |
| Quadruple immunofluorescence of brain tissue: Picture (2) |
VIAAT staining (Alexa Fluor405, blue)
CB1 staining (Alexa Fluor488, green) VIP staining (Cy3, red) DGLα staining (Alexa Fluor647, white) |
There are two subtypes of GABAergic basket cells that express cannabinoid receptors CB1 and govern the pyramidal cell somata one subtype expresses cholecystokinin (CCK), and the other type expresses vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP). This quadruple immunofluorescence staining shows the lack of DGLα (white) around the -positive nerve terminals (red) that strongly express CB1 (green) and VIAAT (blue), indicating that the VIP-positive nerve terminals are not involved in the formation of invaginating synapses. Scale bar: 5 μm.
Imaging system:
Microscope: Biological Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope FV1200
Objective: PLAPON60XOSC (60X, NA: 1.4)
Diode laser: 405 nm, 473 nm, 559 nm, 647 nm
Image data courtesy of:
Masahiko Watanabe, M.D., Ph.D.
Departments of Anatomy, Hokkaido University Graduate School of Medicine
Reference:
J Neurosci. 2015 Mar 11;35(10):4215-28. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4681-14.2015.
Conclusion
Quadruple immunofluorescence for multiple functional molecules and cell markers as shown in Picture (1) and (2) can provide detailed information on cell expression and subcellular localization, which includes the codependent or independent relationship between related functional cells and intercellular spatial distances. Significantly, the detection sensitivity and the resolution of microscopes as well as the optical performance of objective lenses that can minimize chromatic aberrations are important factors in achieving the aims of immunofluorescence.
| PLAPON60×OSC UPLSAPO60×O |
Verwendete Produkte
wurde erfolgreich zu Ihren Lesezeichen hinzugefügt
Maximum Compare Limit of 5 Items
Please adjust your selection to be no more than 5 items to compare at once
Not Available in Your Country
Sorry, this page is not
available in your country.